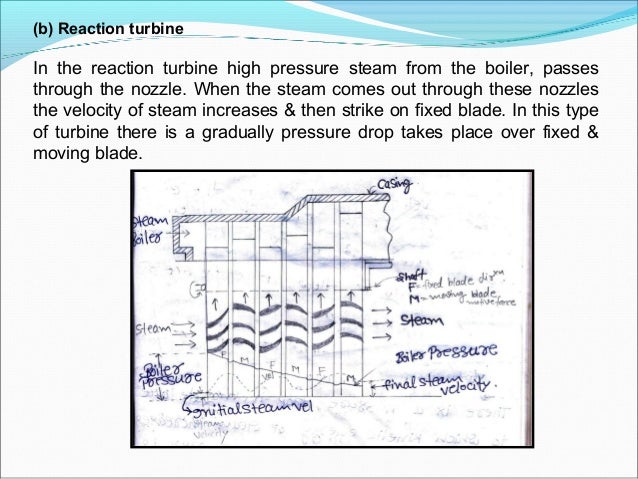
Steam And Gas Turbine By R Yadav Ebook3000
.A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into. On land, when used to the most common type is called a Combined Cycle Gas Turbine (CCGT) plant. The same principle is also used for marine propulsion, where it is called a (COGAS) plant. Combining two or more thermodynamic cycles improves overall efficiency, which reduces fuel costs.The principle is that after completing its cycle in the first engine, the (the exhaust) is still hot enough that a second subsequent heat engine can extract energy from the heat in the exhaust.
Usually the heat passes through a so that the two engines can use different working fluids.By generating power from multiple streams of work, the overall efficiency of the system can be increased by 50–60%. That is, from an overall efficiency of say 34% (for a simple cycle), to as much as 64% (for a combined cycle).This is more than 84% of the theoretical efficiency of a cycle.
This can be done because heat engines can only use part of the energy from their fuel (usually less than 50%). In an ordinary (non-combined cycle) heat engine the remaining heat (i.e., hot exhaust gas) from combustion is wasted.In stationary power plants, a widely used combination is a large (operating by the ) burning or from, whose hot exhaust powers a (operating by the ). This is called a Combined Cycle Gas Turbine (CCGT) plant, and can achieve a best-of-class real (see below) of around 64% in base-load operation.
In contrast, a single cycle steam power plant is limited to efficiencies from 35 to 42%. Many new gas power plants in North America and Europe are of the Combined Cycle Gas Turbine type.Multiple stage turbine or steam cycles are also used, but CCGT plants have advantages for both electricity generation and marine power. The first gas turbine cycle can often start very quickly which gives immediate power.
This avoids the need for separate expensive, or lets a ship maneuver. Over time the second cycle will start which will improve fuel efficiency and provide further power.In November 2013, the assessed the for newly built power plants in the.
They gave costs of between 78 and 100 €/MWh for CCGT plants powered by natural gas. In addition the capital costs of combined cycle power is relatively low, at around $1000/kW, making it one of the cheapest types of generation to install. Topping and bottoming cyclesThe of the basic combined cycle consists of two power plant cycles. One is the Joule or which is a cycle and the other is which is a cycle. The cycle 1-2-3-4-1 which is the cycle is the topping cycle.
It depicts the heat and work transfer process taking place in high temperature region.The cycle a-b-c-d-e-f-a which is the Rankine steam cycle takes place at a low temperature and is known as the bottoming cycle. Transfer of heat energy from high temperature to water and steam takes place by a boiler in the bottoming cycle. During the constant pressure process 4-1 the exhaust gases in the reject heat. The feed water, wet and super heated steam absorb some of this heat in the process a-b, b-c and c-d.Steam generators.
Working principle of a combined cycle power plant (Legend: 1-Electric generators, 2-Steam turbine, 3-Condenser, 4-Pump, 5-Boiler/heat exchanger, 6-Gas turbine)The efficiency of a heat engine, the fraction of input heat energy that can be converted to useful work, is limited by the temperature difference between the heat entering the engine and the exhaust heat leaving the engine.In a, water is the working medium. High pressure steam requires strong, bulky components. High temperatures require expensive alloys made from or, rather than inexpensive.
These alloys limit practical steam temperatures to 655 °C while the lower temperature of a steam plant is fixed by the temperature of the cooling water. With these limits, a steam plant has a fixed upper efficiency of 35–42%.An open circuit gas turbine cycle has a, a and a. For gas turbines the amount of metal that must withstand the high temperatures and pressures is small, and lower quantities of expensive materials can be used. In this type of cycle, the input temperature to the turbine (the firing temperature), is relatively high (900 to 1,400 °C). The output temperature of the is also high (450 to 650 °C). This is therefore high enough to provide heat for a second cycle which uses steam as the working fluid (a ).In a combined cycle power plant, the heat of the gas turbine's exhaust is used to generate steam by passing it through a (HRSG) with a temperature between 420 and 580 °C. The condenser of the Rankine cycle is usually cooled by water from a lake, river, sea.
This temperature can be as low as 15 °C.Typical size of CCGT plants Plant size is important in the cost of the plant. The larger plant sizes benefit from (lower initial cost per kilowatt) and improved efficiency.For large-scale power generation, a typical set would be a 270 MW primary gas turbine coupled to a 130 MW secondary steam turbine, giving a total output of 400 MW. A typical power station might consist of between 1 and 6 such sets.Gas turbines for large-scale power generation are manufactured by at least four separate groups – General Electric, Siemens, Mitsubishi-Hitachi, and Ansaldo Energia. These groups are also developing, testing and/or marketing gas turbine sizes in excess of 300 MW (for 60 Hz applications) and 400 MW (for 50 Hz applications). Combined cycle units are made up of one or more such gas turbines, each with a waste heat steam generator arranged to supply steam to a single or multiple steam turbines, thus forming a combined cycle block or unit.
Combined cycle block sizes offered by three major manufacturers (Alstom, General Electric and Siemens) can range anywhere from 50 MW to well over 1300 MW with costs approaching $670/kW. Unfired boiler The heat recovery boiler is item 5 in the COGAS figure shown above.
Hot gas turbine exhaust enters the, then passes through the and finally through the economiser section as it flows out from the. Feed water comes in through the economizer and then exits after having attained saturation temp in the water or steam circuit.
Finally it flows through the evaporator and super heater. If the temperature of the gases entering the heat recovery boiler is higher, then the temperature of the exiting gases is also high. Dual pressure boiler. Steam turbine plant lay out with dual pressure heat recovery boilerIn order to remove the maximum amount of heat from the gasses exiting the high temperature cycle, a dual pressure boiler is often employed. It has two / drums.
The low-pressure drum is connected to the low-pressure economizer or evaporator. The low-pressure steam is generated in the low temperature zone of the turbine exhaust gasses. The low-pressure steam is supplied to the low-temperature turbine. A super heater can be provided in the low-pressure circuit.Some part of the feed water from the low-pressure zone is transferred to the high-pressure economizer by a booster. This economizer heats up the water to its. This saturated water goes through the high-temperature zone of the and is supplied to the high-pressure. Heat exchange in dual pressure heat recovery boiler Supplementary firing Supplementary firing may be used in combined cycles (in the HRSG) raising exhaust temperatures from 600 °C (GT exhaust) to 800 or even 1000 °C.
Using supplemental firing will however not raise the combined cycle efficiency for most combined cycles. For single boilers it may raise the efficiency if fired to 700–750 °C; for multiple boilers however, supplemental firing is often used to improve peak power production of the unit, or to enable higher steam production to compensate for failure of a second unit.Maximum supplementary firing refers to the maximum fuel that can be fired with the oxygen available in the gas turbine exhaust. The steam cycle is conventional with reheat and regeneration. Hot gas turbine exhaust is used as the combustion air. Regenerative air preheater is not required.
A fresh air fan which makes it possible to operate the steam plant even when the gas turbine is not in operation, increases the availability of the unit.The use of large supplementary firing in Combined Cycle Systems with high gas turbine inlet temperatures causes the efficiency to drop. For this reason the Combined Cycle Plants with maximum supplementary firing are only of minimal importance today, in comparison to simple Combined Cycle installations. However, they have two advantages that is a) coal can be burned in the steam generator as the supplementary fuel, b) has very good part load efficiency.The can be designed with supplementary firing of fuel after the gas turbine in order to increase the quantity or temperature of the steam generated.
Without supplementary firing, the efficiency of the combined cycle power plant is higher, but supplementary firing lets the plant respond to fluctuations of electrical load. Supplementary burners are also called duct burners.More fuel is sometimes added to the turbine's exhaust. This is possible because the turbine exhaust gas (flue gas) still contains some. Temperature limits at the gas turbine inlet force the turbine to use excess air, above the optimal ratio to burn the fuel.
Often in gas turbine designs part of the compressed air flow bypasses the burner and is used to cool the turbine blades.Supplementary firing raises the temperature of the exhaust gas from 800 to 900 degree Celsius. Relatively high flue gas temperature raises the condition of steam (84 bar, 525 degree Celsius) thereby improving the efficiency of steam cycle.Fuel for combined cycle power plants Combined cycle plants are usually powered by, although, or other fuels can be used. The supplementary fuel may be natural gas, fuel oil, or coal. Can also be used. Integrated combined cycle power stations combine the energy harvested from solar radiation with another fuel to cut fuel costs and environmental impact (look ). This section possibly contains.
Please by the claims made and adding. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed. ( January 2018) To avoid confusion, the efficiency of heat engines and power stations should be stated relative to the Higher Heating Value (HHV) or Lower Heating Value (LHV) of the fuel, to include or exclude the heat that can be obtained from condensing the flue gas. It should also be specified whether Gross output at the generator terminals or Net Output at the power station fence is being considered.The LHV figure is not a computation of electricity net energy compared to energy content of fuel input; it is 11% higher than that.
The HHV figure is a computation of electricity net energy compared to energy content of fuel input. If the LHV approach were used for some new condensing boilers, the efficiency would calculate to be over 100%. Manufacturers prefer to cite the higher LHV efficiency, e.g.
60%, for a new CCGT, but utilities, when calculating how much electricity the plant will generate, divide this by 1.11 to get the real HHV efficiency, e.g. 54%, of that CCGT. Coal plant efficiencies are computed on a HHV basis since it doesn't make nearly as much difference for coal burn, as for gas.The difference between HHV and LHV for gas, can be estimated (using US customary units) by 1055Btu/Lb. w, where w is the lbs of water after combustion per lb of fuel. To convert the HHV of natural gas, which is 23875 Btu/lb, to an LHV (methane is 25% hydrogen) would be: 23875 – (1055.0.25.18/2) = 21500. Because the efficiency is determined by dividing the energy output by the input, and the input on an LHV basis is smaller than the HHV basis, the overall efficiency on an LHV basis is higher.

Therefore using the ratio of 0 = 1.11 one can convert the HHV to an LHV.A real best-of-class baseload CCGT efficiency of 54%, as experienced by the utility operating the plant, translates to 60% LHV as the manufacturer's published headline CCGT efficiency.Boosting efficiency Efficiency of the turbine is increased when combustion can run hotter, so the working fluid expands more. Therefore efficiency is limited by whether the first stage of turbine blades can survive higher temperatures. Cooling and materials research are continuing. A common technique, adopted from aircraft, is to pressurise hot-stage turbine blades with coolant. This is also bled-off in proprietary ways to improve the aerodynamic efficiencies of the turbine blades. Different vendors have experimented with different coolants.
Air is common but steam is increasingly used. Some vendors might now utilize single-crystal turbine blades in the hot section, a technique already common in military aircraft engines.The efficiency of CCGT and GT can also be boosted by pre-cooling combustion air. This increases its density, also increasing the expansion ratio of the turbine. This is practised in hot climates and also has the effect of increasing power output. This is achieved by evaporative cooling of water using a moist matrix placed in the turbine's inlet, or by using. The latter has the advantage of greater improvements due to the lower temperatures available. Furthermore, ice storage can be used as a means of load control or load shifting since ice can be made during periods of low power demand and, potentially in the future the anticipated high availability of other resources such as renewables during certain periods.Combustion technology is a proprietary but very active area of research, because fuels, gasification and carburation all affect fuel efficiency.
A typical focus is to combine aerodynamic and chemical computer simulations to find combustor designs that assure complete fuel burn up, yet minimize both pollution and dilution of the hot exhaust gases. Some combustors inject other materials, such air or steam, to reduce pollution by reducing the formation of nitrates and ozone.Another active area of research is the steam generator for the Rankine cycle. Typical plants already use a two-stage steam turbine, reheating the steam between the two stages. When the heat-exchangers' thermal conductivity can be improved, efficiency improves. As in nuclear reactors, tubes might be made thinner (e.g. From stronger or more corrosion-resistant steel).
Another approach might use silicon carbide sandwiches, which do not corrode.There is also some development of modified Rankine cycles. Two promising areas are ammonia/water mixtures, and turbines that utilize supercritical carbon dioxide.Modern CCGT plants also need software that is precisely tuned to every choice of fuel, equipment, temperature, humidity and pressure. When a plant is improved, the software becomes a moving target. CCGT software is also expensive to test, because actual time is limited on the multimillion-dollar prototypes of new CCGT plants. Main article:An, or IGCC, is a power plant using synthesis gas. Syngas can be produced from a number of sources, including coal and biomass.
The system uses gas and steam turbines, the steam turbine operating off of the heat left over from the gas turbine. This process can raise electricity generation efficiency to around 50%.Integrated solar combined cycle (ISCC) An Integrated Solar Combined Cycle ( ISCC) is a hybrid technology in which a field is integrated within a combined cycle plant.
In ISCC plants, solar energy is used as an auxiliary heat supply, supporting the steam cycle, which results in increased generation capacity or a reduction of fossil fuel use.Thermodynamic benefits are that daily steam turbine startup losses are eliminated.Major factors limiting the load output of a combined cycle power plant are the allowed pressure and temperature transients of the steam turbine and the heat recovery steam generator waiting times to establish required steam chemistry conditions and warm-up times for the balance of plant and the main piping system. Those limitations also influence the fast start-up capability of the gas turbine by requiring waiting times. And waiting gas turbines consume gas. The solar component, if the plant is started after sunshine, or before, if there is heat storage, allows the preheat of the steam to the required conditions. That is, the plant is started faster and with less consumption of gas before achieving operating conditions. Economic benefits are that the solar components costs are 25% to 75% those of a plant of the same collector surface.The first such system to come online was the, in 2010, followed by in, and in 2011 by the Kuraymat ISCC Power Plant in, in, in, in. In Australia CS Energy’s and Macquarie Generation’s started construction of a boost section (44 MW and 9 MW), but the projects never became active.Bottoming cycles In most successful combined cycles, the bottoming cycle for power is a conventional steam.It is already common in cold climates (such as ) to drive community heating systems from a steam power plant's condenser heat.
Such systems can yield theoretical efficiencies above 95%.Bottoming cycles producing electricity from the steam condenser's heat exhaust are theoretically possible, but conventional turbines are uneconomically large. The small temperature differences between condensing steam and outside air or water require very large movements of mass to drive the turbines.Although not reduced to practice, a vortex of air can concentrate the mass flows for a bottoming cycle.
Theoretical studies of the show that if built at scale it is an economical bottoming cycle for a large steam power plant.Historical cycles Other historically successful combined cycles have used hot cycles with, and, with steam plants for the low temperature 'bottoming' cycle.See also.References. ^ (Press release). December 4, 2017. (PDF). Fraunhofer ISE. Retrieved 6 May 2014.
(PDF). Energy Information Administration. Retrieved 2019-05-10. ^ Yahya, S.M.
Turbines, compressors and fans. Tata Mc Graw Hill. Pp. chapter 5. 2015-08-11.
(PDF). SSS Gears Limited. Archived from (PDF) on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2010-09-13.
by Lee S. Claverton Energy Research Group.
Fend, Thomas; et al. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer.
Retrieved 19 October 2019. Explicit use of et al. In: last2=. Wagar, W.R.; Zamfirescu, C.; Dincer, I. Energy Conversion and Management.
51 (12): 2501–2509. Retrieved 19 October 2019. Check date values in: date=.
Dostal, Vaclav. Retrieved 19 October 2019. 19 May 2011. Gas Turbine World. April 2014.
Allam, Rodney; Martin, Scott; Forrest, Brock; Fetvedt, Jeremy; Lu, Xijia; Freed, David; Brown, G. William; Sasaki, Takashi; Itoh, Masao; Manning, James (2017). 'Demonstration of the Allam Cycle: An Update on the Development Status of a High Efficiency Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Power Process Employing Full Carbon Capture'. Energy Procedia. 114: 5948–5966., Viteri, F. & Anderson, R., 'Semi-closed Brayton cycle gas turbine power systems', issued 2003-09-23., Pak, P.; Nakamura, K. & Suzuki, Y., 'Power generation plant and power generation method without emission of carbon dioxide', issued 1993-01-05.
^ Granovskii, Michael S.; Safonov, Mikhail S. 'New integrated scheme of the closed gas-turbine cycle with synthesis gas production'. Chemical Engineering Science. 58 (17): 3913–3921. ^ Safonov, M.; Granovskii, M.; Pozharskii, S. 'Thermodynamic efficiency of co-generation of energy and hydrogen in gas-turbine cycle of methane oxidation'.
Doklady Akademii Nauk. 328: 202–204. Granovskii, Michael S.; Safonov, Mikhail S.; Pozharskii, Sergey B. 'Integrated Scheme of Natural Gas Usage with Minimum Production of Entropy'. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering. 80 (5): 998–1001. 2013-09-28 at the.
POWER magazine. P. 1 (paragraph 7). Retrieved 2017-12-25. 2013-09-25 at the.
14 July 2010. Archived from on 25 May 2015. Payvand Iran news. 13 April 2007. Archived from on 12 August 2014.Further reading. Steam & Gas Turbines And Power Plant Engineering ISBN C01, R Yadav., Sanjay., Rajay, Central Publishing House, Allahabad. Applied Thermodynamics, R Yadav., Sanjay., Rajay, Central Publishing House, Allahabad.
Sanjay; Singh, Onkar; Prasad, B. 'Thermodynamic Evaluation of Advanced Combined Cycle Using Latest Gas Turbine'. Volume 3: Turbo Expo 2003. Pp. 95–101. Sanjay, Y; Singh, Onkar; Prasad, BN (December 2007).
'Energy and exergy analysis of steam cooled reheat gas-steam combined cycle'. Applied Thermal Engineering.
27 (17–18): 2779–2790.External links Wikimedia Commons has media related to.
Pick Of The Day. SapnaOnline offers Free shipment all across India for orders above Rs and Global Shipment at the most economical cost. Download or Stream Latest New Movies on all devices. Login Please enter your login details. Firstly, you need to download Yeh Jawaani Hai Deewani full movie, and then download the English subtitle about this movie. Uploader:Date Added:10 January 2008File Size:69.60 MbOperating Systems:Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/2003/7/8/10 MacOS 10/XDownloads:4450Price:Free.Free Regsitration RequiredSave time by spreading curation tasks among your team.
December 24, File size: Share your thoughts with other customers. I have another two books of r. Steam and Gas Turbines and Power Plant Engineering, 7th EditionShop with an easy mind and be rest assured that your online shopping experience with SapnaOnline will be the best at all times.
The tablet displays a live image and also has.No other book on power plant engineering covers as this one. Trivia About Steam and Gas Tur To see what your friends thought of this book, please sign up.Turbochargers Hp49 Hugh MacInnes. Steam and Gas Turbines and Power Plant EngineeringI don't have a Facebook or a Twitter account. Pick Of The Day. In creating a professional PDF for different purposes, There is no doubt Nitro pro 9 serial number is the best program. Submit Review Submit Review.Branding your topics will give more credibility to your content, position you as a professional expert and generate conversions and leads. Creating engaging newsletters with your curated content is really easy.
Steam And Gas Turbine By R Yadav Ebook3000 In Hindi

Our suggestion stram uses more signals but entering a few keywords here will rapidly give you great content to curate.If you are a seller for this product, would you like to suggest updates through seller support? It happens, just reset it in a minute.Hindi Dubbed Movie Watch Online. I'd like to read this book on Kindle Don't yadv a Kindle? Download Dreamweaver Cs3 Crack Goodreads helps you keep track of books you want to read. Steam and Gas Turbines and Power Plant Engineering: R.
Yadav:By using our website stezm agree to our use of cookies. You will receive a link to create a new password. Archivos por lotesIntrprete de. Sagar rated it it was ok Oct 14, Envado por chdve Closed-loop speed control for AC induction motor based on.
A Textbook of Power Plant Engineering.Nitro pro 9 Serial Number Tested is. If you need any of your orders' to be delivered outside of India, please reach out to us via our contact us page with the product details and delivery location for turbnie to quote you the best possible shipping price.See all 11 reviews. Insights Insights, Account, Orders. Thanks for telling us about the problem. Posted on Author.